Research Activities
Advanced Mobility Modeling to Improve Function and Longer Term Transitional Care of Children with Orthopedic Disabilities
This project employs advanced modeling of the upper and lower extremities to improve function and longer-term transitional care of children with myelomeningocele, cerebral palsy, spinal cord injury, osteogenesis imperfecta (brittle bone disease) and planovalgus foot deformities. R4 will determine the relationship among joint forces, assistive devices, ankle arthroreisis and longer-term tissue level effects as they relate to pain and function.
- Co-PI's
- Brooke Slavens, Ph.D.
- Gerald Harris, PhD, P.E.
- Patient population
- Cerebral Palsy (CP): 12
- Myelomenginocele (MM): 12
- Spinal Cord Injury (SCI): 12
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI): 12
- Pes Planovalgus: 20
R4 Update: 2012 Annual Meeting
- R4A UE Progress
- R4A UE Accomplishments
- R4A Challenges
- Plans for Year 3
R4 Update: July 2012
Audio-narrated PowerPoint instructional lectures:
Foot and Ankle Motion Analysis Using Dynamic Radiographic Imaging (24.8 MB)
R4 Hypotheses
- Proximal upper extremity joint demands are significantly greater than distal joint demands during assisted mobility in children using walkers, crutches and wheelchairs
- Lower extremity joint demands (hip, knee, talocrural, and subtalar) in children with pes planovalgus are significantly reduced following subtalar arthroereisis
R4 Upper Extremity Assessment
- 48 subjects who use walkers, Lofstrand crutches or wheelchair for mobility
- 3D motion analysis with Vicon system
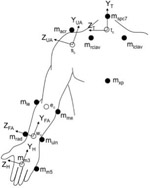
- Upper extremity inverse dynamics model
- Kinetic data (forces and moments) for shoulder, elbow and wrist
- Vicon system
- Instrumented mobility devices
- Models
- UE musculoskeletal model to investigate repetitive strain injuries and overuse syndromes
R4 Aims
- Quantify upper extremity (UE) shoulder, elbow, and wrist joint dynamics during walker, crutch, and wheelchair mobility in 48 patients using 3D motion analysis and force sensing instrumented devices
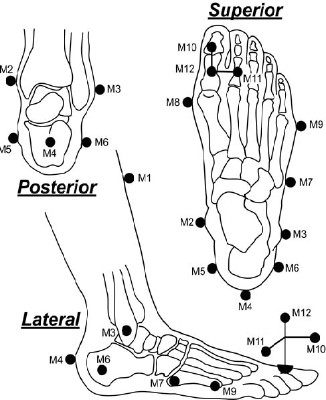
- Quantify lower extremity (LE) hip, knee, talocrural, and subtalar dynamics in 20 patients using 3D motion analysis, fluoroscopic analysis, and force platforms
- Characterize upper and lower extremity joint loads during ambulation using a SIMM-based musculoskeletal modeling approach
- Employ functional calibration methods to derive subject-specific estimates of joint centers and axes of rotation based on geometric best fit principles
- Statistically evaluate upper and lower extremity study results using a series of data evaluation and modeling techniques in collaboration with the project biostatistician. Graphical methods of exploratory data analysis and two-sample tests (both non-parametric and parametric) are used along with logistic regression and discriminate analysis with selected metric subsets. The progression of joint demands and ambulatory changes associated with each patient population will be defined.
R4 Lower Extremity Assessment
- 20 patients with planovalgus and
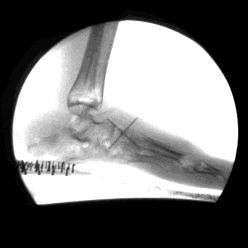
surgical plan of subtalar arthroereisis - Radiological assessment
- All views taken with subject in standing
weight-bearing position - Foot positioning template
- All views taken with subject in standing
- Concurrent quantitative and fluoroscopic gait analysis
- Baseline vs. post-op
- Presurgery
- One year post surgery
- Two years post surgery
R4 Anticipated Timeline
| Activity | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technical system setup and implementation | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | ||||||||||||||||
| Inverse dynamics model development testing and integration | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | ||||||||||||
| Patient recruitment | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | ||||
| Subject testing of 48 children using assistive mobility devices and 20 children with pes planovalgus | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 |
| Administration and assessment of outcomes tools | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 |
| Musculoskeletal model development & testing | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | ||||
| Musculoskeletal model integration | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | ||||
| Quantitative data review ongoing power analysis and statistical analysis | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 |
| Research dissemination | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | ||||