4 Researchers: Overview
This RERC serves as a national center focused on advanced engineering research and development of innovative technologies addressing children with orthopedic disabilities. Our development, training and knowledge dissemination plans help transfer and commercialize our efforts to offer new tools, better technologies, and improved evidence-based treatment strategies for children with orthopedic disabilities.
Importance of the Problem
National Institute on Disability and Rehabilitation Research (NIDRR)The new paradigm of disability is integrative and holistic, and focuses on the whole person functioning in an environmental context. This new paradigm of disability is reflected in the ADA and sets a goals framework for research, policy, and the delivery of services and supports relative to disability.
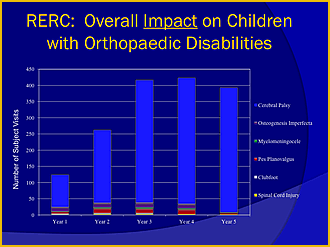
Patient Contacts that Will Result from the Total RERC Effort
Click for larger view
Over 95% of the patient contacts are the result of research projects R1 through R4. The remaining 5% are the result of design projects D1 through D4.
Need and Target Population
- 6.1% (4 million) of the U.S. population under 18 years of age has limited function*
- 4% (2.3 million) of two-parent families contain at least one child with a disabling condition
| Chronic Disabling Condition | Number |
|---|---|
| Spinal Cord Injury | 262,000** |
| Orthopedic Impairments | 144,000 |
| Cerebral Palsy | 99,000 |
| Osteogenesis Imperfecta | 35,000** |
| Clubfoot | 2,140 per year |
| Pes Planovalgus | 1 in 9 |
| Myelomeningocele | 17,000 |
*: > for children aged 21 yrs. and younger/NIDRR;
** : adults included
Overall Anticipated Beneficial Impacts – Research
- Fracture risk prediction in children with osteogenesis imperfecta (brittle bone) (R1)
- Quantitative clubfoot correction models/guidelines based on tissue and cast characteristics (R1)
- Prediction of sensorimotor and CNS adaptations to orthopedic treatment (R2)
- Brain plasticity responses to robotic intervention in the upper and lower extremities (R2)
- Reduced declines in mobility with home-based robot- assisted therapy and tele-assessment (R3)
- Identification of at risk joint demands in the upper extremities of children who use assistive devices for mobility (R4)
- Improved subtalar kinetics and muscle metrics associated with corrective arthroereisis (arthrorisis) implantation for planovalgus foot deformity (R4)
Overall Anticipated Beneficial Impacts – Development
- Development of a novel elliptical machine to improve lower extremity stability and control in the axial and frontal planes in children with patellofemoral instability and cerebral palsy (D1)
- Incorporation of attractive and intuitive VR training games as a biofeedback mechanism during elliptical training (D1)
- Development of a unique 3D robotic gait training system with controlled forces in the sagittal and frontal planes for naturalistic stepping during treadmill training (D2)
- Development of a biplanar fluoroscopic system for in vivo foot and ankle motion analysis (D3)
- Development of a customized, dynamic orthosis to benefit children with severe planovalgus foot deformity utilizing computer based, rapid prototyping techniques (D4)